[Research Interests]

Computational Mechanics Including:
Development of New High-Order Numerical Methods with Optimal Accuracy for Partial Differential Equations
New Finite Element Algorithms for Symmetric Structures, Structural Dynamics and Discrete(Finite) & Continuum(Infinity) Mechanics Problems
Time−Integration Methods for Elasto-dynamics Including Chaotic-phenomena Problems
Nonlinear Problems with Finite Thermal, Elastic and Plastic Strains, Nonlinear Problems with Group-theoretic Bifurcation with Symmetric Group (with foldable/Deployable, Origami, Post-buckling)
Numerical Simulation of Different Engineering Problems
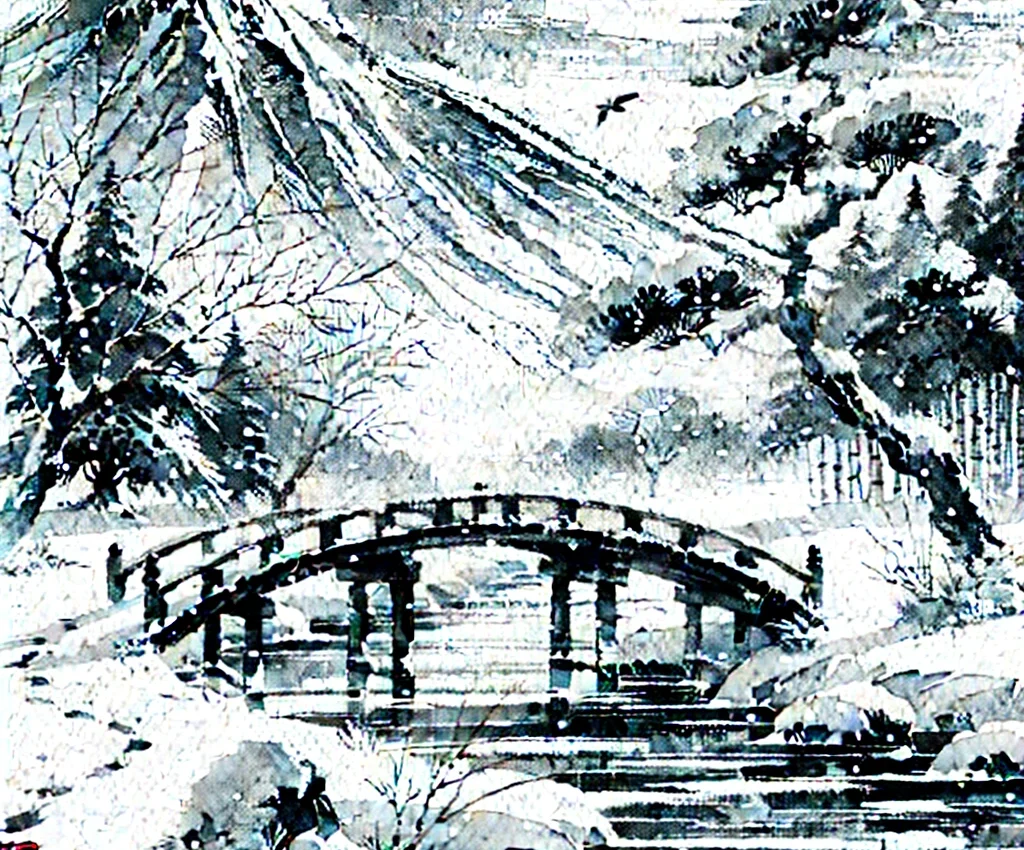
[構造安定性]
座屈やカオス現象は「分岐」と呼ばれ、構造物の不安定性を伴う非線形力学問題である。
構造工学と非線形科学の両方に関わる構造安定性を研究しています。
特に、構造物が崩壊する事象は'catastrophy' と呼ばれます。
例えば、球体や円筒シェルなどの弾性構造系が亜臨界的に安定性を失う問題は大切です。
その際、'座屈'と呼ばれ、対称性も失います(Symmetry-breaking)。
このような構造は、欠陥や衝撃が線形安定性のしきい値をはるかに下回る荷重点で座屈崩壊を引き起こすため、設計と実現象の予測が難しいです。
構造的不安定現象への関心は、実用的な安定性評価には「分岐解析」、「幾何学的非線形の計算力学」、「確率論的アプローチ」と「不完全性感度による分析」が必要です。
ここで、座屈していない座屈パターンと完全に発達した座屈パターンのエネルギーが等しく、局所的な状態のエネルギーを持ち、安定した状態と不安定な状態が蛇行する荷重-たわみ経路上で度々複数発生します。
最新技術は、理論的、数値的、実験的方法で調べられています。
有限要素近似の弧長法(パス追跡)は、複雑な局所状態の様々な釣合い経路を有します。
多重特異点を持つような鞍状型の全ポテンシャルエネルギー観点、オリガミを用いた円筒座屈問題、新しい展開構造の設計創生、対称性破れ事象モデル、幾何学的対称性と構造強度の関係、後座屈メカニズムなどを探求しています。
その他に、折り紙をヒントとした周期構造と展開する多重折畳み構造体やスケール問題における幾何構造の周期性と強度の関係を(非線形)平衡問題における構造最適化やアルゴリズムを創造中です。
[Structural stability]
Buckling and chaos phenomena are called “bifurcation” and are nonlinear mechanical problems with structural instability.
Mainly on "structural stability" involved in both structural engineering and nonlinear science. In particular, the phenomenon of structure collapse is called 'Catastrophe'. For example, the problem of sub-critically unstable elastic structural systems such as spheres and cylindrical shells is serious. At that time, it is called 'buckling' and loses symmetry (Symmetry-breaking). Such structures are difficult to design and predict actual phenomena because defects and impacts cause buckling collapse at load points well below the linear stability threshold. Interest in structural instability requires a "stochastic approach" and an "incompleteness sensitivity analysis" for practical stability assessment. Here, the energy of the non-buckling pattern and the fully developed buckling pattern are equal, they have the energy of the local state, and the stable state and the unstable state meandering load-often on the deflection path. It occurs more than once. The latest technology is being investigated analytically, numerically and experimentally. The arc length method (path tracking) of finite element approximation has various equilibrium paths of complex local states. Second, the numerical implementation of the saddle-shaped energy method predicts the energy barriers in which the buckling process occurs. Recent developments also suggest ways to reproduce computationally and experimentally.