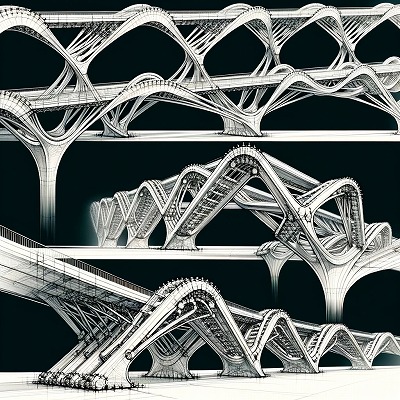


現代社会において、自然災害は人々の生活に大きな影響を与えます。人命救助やインフラの復旧など、多岐にわたる問題に対処するためには、迅速で的確な対応が求められます。そのために、人工知能(AI)技術を活用した災害対策が注目されています。AI技術によって、災害発生時の早期警戒や人命救助、被災地の復旧支援など、多くの課題が解決される可能性があります。
まず、災害発生時の早期警戒について考えてみましょう。災害の発生を予測するためには、気象データや地震データなどの情報を収集し、分析する必要があります。しかし、これらのデータは膨大な量になるため、人手での分析は困難です。ここで、AI技術が役立ちます。AI技術を用いることで、大量のデータを高速かつ正確に分析し、災害発生の予測を行うことが可能になります。また、AI技術を活用することで、過去の災害情報を蓄積し、将来の災害対策に役立てることもできます。
次に、人命救助について考えてみましょう。災害発生時には、多くの人が救助を必要とします。しかし、被災地にある道路や橋などのインフラが破壊されると、救助活動が困難になることがあります。ここで、AI技術を用いることで救助活動の効率化が可能になります。例えば、無人飛行機やロボットを活用することで、人間が到達できない場所にもアクセスできるようになります。また、人命救助においては、迅速かつ正確な情報共有が必要となります。AI技術を活用することで、被災地の情報をリアルタイムで共有し、より迅速な救助活動を実現することができます。
私たちは災害リスクに対する意識を高め、適切な備えを行うことが重要であり、また、人命救助には迅速な行動が必要であるということも強調しました。 インフラの早期復旧は人命救助に必要不可欠であり、優先的に導入すべきことの一つである。
最後に、私たちは自分たち一人一人が災害に備え、自助・共助の精神を持つことが大切です。災害対策は社会全体で取り組むべき問題であり、自治体や地域・企業だけでなく、個人も参加し、安全な社会を実現することが必要なのです。これまでの教訓を活かし各地域整備局、道の駅や学校など避難所に指定される場所に、ハード&ソフトのポスト災害インフラ復旧ツールがあるといいですね。災害から逃れられない国土に住む我々自身の防災技術を高めながら、産業基盤を構築することも次世代への大切なビジョンです。次の大きな災害が来る前に。
Certainly. Here is a summary of what I have learned and written about: Natural disasters such as earthquakes, typhoons, and floods can cause damage to infrastructure, including bridges. The repair and reconstruction of these bridges are important for ensuring public safety and aiding in disaster relief efforts. However, the process of repairing or rebuilding a bridge can be time-consuming and costly, which may lead to delays in relief efforts. In order to address this challenge, the concept of a modular bridge (MB) has been proposed. An MB is a prefabricated bridge that can be quickly installed and used as a temporary or permanent solution to bridge damage. There are several advantages to using an MB. First, the modular design of the bridge allows for quick and easy installation, reducing the time needed for repair or reconstruction. Second, the prefabrication of the bridge components means that they can be mass-produced and transported to the site of the damaged bridge, further speeding up the repair process. Finally, the modular design also allows for flexibility in bridge design, making it possible to customize the bridge to meet the specific needs of the location and disaster situation. However, there are also some challenges and limitations associated with the use of MBs. For example, the modular design may not be as structurally sound as a traditional bridge, especially for long-term use. In addition, the cost of producing and transporting the prefabricated components may be higher than that of traditional bridge construction methods. Finally, there may be resistance to the adoption of MBs due to a lack of familiarity with the technology and concerns over their reliability. Overall, the development and adoption of MBs has the potential to improve disaster relief efforts and ensure public safety in the aftermath of natural disasters. While there are challenges to their use, continued research and development may help to address these challenges and make MBs a viable solution for bridge repair and reconstruction in the future.

Mobile Bridges, or MB for short, are a type of bridge that can be quickly and easily deployed to span a variety of gaps. Unlike traditional bridges, which are typically stationary structures, MBs can be moved to different locations as needed. They are a versatile and flexible solution for a wide range of applications, including disaster relief, military operations, and temporary infrastructure needs.
The concept of MBs has been around for several decades, but recent advances in technology have made them more practical and efficient than ever before. One notable development is the use of lightweight materials, such as aluminum, which makes the bridges easier to transport and deploy. Additionally, the use of modular construction techniques allows MBs to be assembled quickly and without the need for heavy equipment.
One of the key advantages of MBs is their mobility. Because they can be quickly assembled and disassembled, they can be used in situations where traditional bridges are not feasible or practical. For example, in disaster relief situations where roads and bridges may be damaged or inaccessible, MBs can be deployed to provide temporary access for emergency responders and aid workers.
MBs are also well-suited for military operations, where speed and agility are crucial. They can be used to quickly span rivers, ravines, and other obstacles, allowing troops to move quickly and safely across difficult terrain. Additionally, MBs can be used to establish temporary bases and infrastructure in remote areas where traditional bridges may not be available.
In recent years, MBs have also been used in a variety of civilian applications. For example, they can be used to provide temporary access to construction sites, allowing workers and equipment to easily move across a gap. They can also be used to provide temporary access for events and festivals, such as music concerts and outdoor markets.
Despite their many advantages, there are some challenges to the widespread adoption of MBs. One of the main challenges is cost. Because they are often custom-designed and manufactured, MBs can be more expensive than traditional bridges. Additionally, there may be regulatory and permitting issues associated with their use in certain locations.
Overall, MBs are a versatile and flexible solution for a wide range of applications. Their mobility and ease of deployment make them a valuable tool in emergency response, operations, and temporary infrastructure needs. As technology continues to advance and costs come down, MBs are likely to become an even more common solution for bridging gaps and providing access in a variety of situations.
Welcome to Our research topics. This is your first post. Edit or delete it, then start writing!